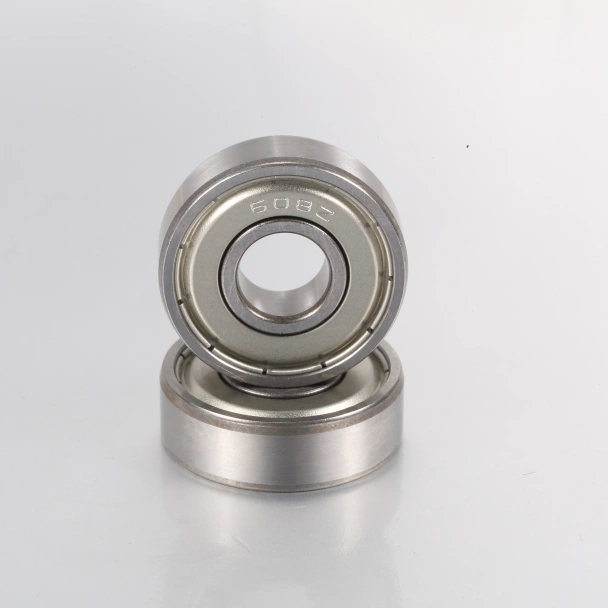
Maintaining Deep Groove Ball Bearings for Optimal Performance
 Nov 19,2024
Nov 19,2024
 WYOO
WYOO
Proper maintenance of deep groove ball bearings is essential to ensure their long - term performance and reliability. Neglecting maintenance can lead to premature failure, increased downtime, and costly repairs. Here are some key maintenance tips for deep groove ball bearings.
Lubrication
Lubrication is perhaps the most critical aspect of bearing maintenance. The right lubricant reduces friction, dissipates heat, and protects the bearing surfaces from wear and corrosion. For deep groove ball bearings, there are two main types of lubricants: grease and oil. Grease lubrication is suitable for applications where the bearing operates at relatively low speeds and temperatures. Grease has the advantage of staying in place and providing long - term lubrication. When choosing grease, consider factors such as the operating temperature range, load conditions, and the type of bearing. Oil lubrication, on the other hand, is preferred for high - speed applications. Oil provides better heat dissipation and lower friction compared to grease. Regularly check the lubricant level and condition. If the lubricant has become contaminated or has lost its viscosity, it should be replaced promptly.

Cleaning
Keeping the bearing clean is also important. Contaminants such as dirt, dust, and metal particles can enter the bearing and cause damage. Before handling the bearing, make sure your hands and the work area are clean. When installing or removing the bearing, use clean tools. If the bearing is in a dirty environment, consider using a protective cover or seal. Periodically clean the bearing using a suitable solvent. However, be careful not to use solvents that can damage the bearing surfaces or the lubricant. After cleaning, dry the bearing thoroughly before reinstalling it.
Monitoring
Regular monitoring of the bearing's performance can help detect potential problems early. Monitor the temperature of the bearing during operation. An increase in temperature can indicate issues such as insufficient lubrication, misalignment, or excessive loads. Use a thermometer or an infrared temperature gun to measure the temperature. Also, listen for any abnormal noises coming from the bearing. Unusual noises such as rattling, squealing, or grinding can





 HOME
HOME Deep Groove Ball Bearings in Industrial Applications
Deep Groove Ball Bearings in Industrial Applications  You May Also Like
You May Also Like






















 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address












 Let’s Talk
Let’s Talk

