Deep Groove vs. Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Which One Should You Choose?
 Dec 22,2025
Dec 22,2025
 Wanyuan
Wanyuan
When designing or maintaining machinery, selecting the correct bearing is the difference between seamless operation and catastrophic failure. The two most common types are Deep Groove Ball Bearings (DGBB) and Angular Contact Ball Bearings (ACBB). While they may look similar, their internal geometries and load-handling capabilities are vastly different.
This comprehensive guide breaks down the differences to help you make an informed engineering choice.
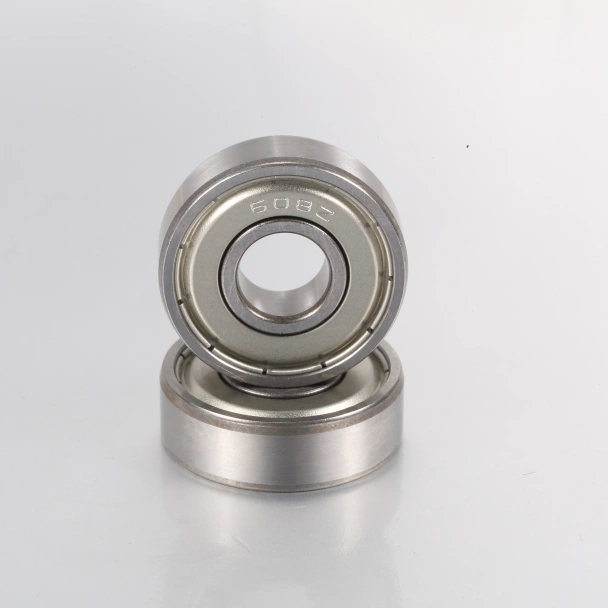
1. What are Deep Groove Ball Bearings?
Deep Groove Ball Bearings are the most widely used bearing type globally. They feature high-quality steel balls that run in deep, symmetrical raceways.
Load Type: Primarily radial loads (perpendicular to the shaft). They can handle limited axial (thrust) loads in both directions.
Key Advantage: Versatility and low friction. They are suitable for high speeds and require minimal maintenance.
Common Applications: Household appliances, electric motors, and office equipment.
2. What are Angular Contact Ball Bearings?
Angular Contact Ball Bearings are engineered for "combined loads." The inner and outer ring raceways are displaced relative to each other along the bearing axis.
Load Type: Combined loads (simultaneous radial and heavy axial loads). The larger the contact angle (typically 15°, 25°, or 40°), the higher the axial load capacity.
Key Advantage: Exceptional rigidity and precision under thrust.
Common Applications: High-speed spindles, centrifugal pumps, and automotive transmissions.
3. Key Differences: At a Glance
Feature Deep Groove Ball Bearings Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Contact Angle 0° (Theoretical) 15°, 25°, 40°
Axial Load Capacity Low to Moderate (Bi-directional) High (Single Direction)
Mounting Can be used individually Often used in pairs (DB, DF, DT)
Precision Standard to High High to Super-Precision
Cost Cost-effective due to mass production Higher due to specialized design
4. Selection Criteria: How to Decide?
When to choose Deep Groove:
Your application involves standard rotation with minimal side-thrust.
You need a cost-effective, "off-the-shelf" solution.
The bearing needs to handle small axial loads from both sides.
When to choose Angular Contact:
The application experiences significant axial force from one direction.
You require high system rigidity (e.g., to prevent shaft deflection).
High-speed precision is a priority, such as in CNC machining.
5. Conclusion
Choosing between deep groove and angular contact ball bearings depends entirely on your application's load profile and precision requirements. While deep groove bearings offer simplicity and economy, angular contact bearings provide the robustness needed for complex, combined-load environments.





 HOME
HOME Rod End Bearings in Construction Equipment
Rod End Bearings in Construction Equipment  You May Also Like
You May Also Like






















 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address











 Let’s Talk
Let’s Talk

